Machine Learning Algorithms & Theories Index
A comprehensive deep dive into algorithmic mechanics, optimization strategies, and deployment patterns spanning GenAI, Time Series, Deep Learning, and Statistical Learning.
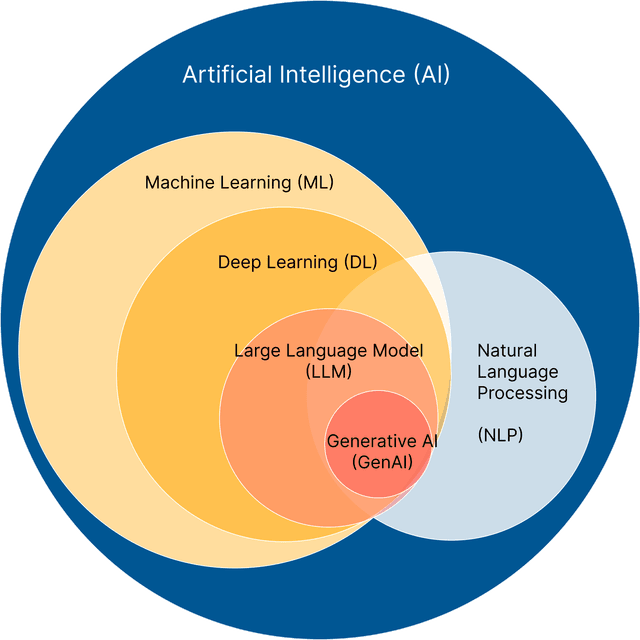
The landscape of Machine Learningspans from robust statistical foundations to the frontiers of generative intelligence.
This section provides a deep dive into the algorithmic mechanics, optimization strategies, and deployment patterns of modern AI.
Categories
- Transformer Architectural Deep Dives:
Explore foundational transformer architectures such as self-attention, GQA, PE, and tokenization. - Generative AI:
Exploring foundational generative models for multi-modal generation (text, image, audio). - Time Series Analysis:
Managing temporal dependencies with the RNN family, including LSTMs, GRUs, and state-space models. - Deep Learning (Discriminative):
Mastering multi-layer perceptrons (MLP) and feed-forward networks for complex feature extraction and classification. - Traditional ML (Statistical Learning):
Leveraging classic models including SVMs, ensemble trees, k-NN, and more for structured data efficiency.
Transformer Architectural Deep Dives
Tokenization Strategies for LLM Applications
Explore the mechanics like BPE and Unigram and how to choose suitable tokenizer for your LLM application
Tokenization is the bridge between human language and machine-readable vectors.
Choosing the right tokenizer impacts an LLM's capabilities. This technical guide breaks down the core architectures and provides a framework for selecting the best one for your task.

Transformer Architecture: Self-Attention & MLOps Guide
Exploring attention and its role in contextual text understanding with walkthrough examples
The transformer model revolutionizes natural language processing (NLP) by processing entire sequences at once, leveraging techniques like self-attention mechanism, positional encodings, and multi-head attention.

Beyond the Window: Benchmarking Positional Encoding (PE) for LLM Extrapolation
Scaling context windows via PE extrapolation on unseen sequence lengths
An architectural deep dive and synthetic benchmark of FAPE, LPE, RPE, and RoPE. Learn how different Positional Encoding methods impact a Transformer's ability to handle sequences 20x longer than its training context.

Grouped Query Attention (GQA): Balancing LLM Quality and Speed
Finding the perfect balance between MHA quality and MQA inference throughput
Grouped-Query Attention (GQA) is a type of attention mechanisms designed to reduce the memory bandwidth requirements and latency during the decoding phase.

Implementing Attention Approximation: Transformer Efficiency & Trade-offsr
Self-attention mechanisms and attention approximation techniques in Transformer
The Transformer architecture, introduced in the “Attention Is All You Need” paper, has revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP). Its core innovation, the self-attention mechanism, allows models to weigh the importance of different parts of the input sequence. However, the standard self-attention mechanism suffers from its computational complexity which scales quadratically (O(N²)) as the length of the input sequence N grows, creating a bottleneck especially in tasks with long N such as document summarization or high-resolution image processing. Attention approximation solve this challenge by reducing the complexity using various techniques.

Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Generative AI
Generative Models are a class of machine learning models designed to learn the underlying patterns and distribution of their training data to generate new, original data samples that are similar to what they were trained on.
Key points include:
- Function: The primary goal is to create new content like text, images, video, audio, or code rather than predicting labels on existing data.
- Training: The model is trained by analyzing a massive amount of data to understand the joint probability distribution of the features in the data.
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN): From Vanilla Minimax to ProGAN
Explore core GAN principles with a walkthrough example and major GAN architectures
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a class of deep learning architectures designed for generative modeling which focuses on generating new, realistic examples from original data.

Autoencoders (AEs): Dense, CNN, and RNN Implementation Guide
Explore the core mechanics of AEs with essential regularization techniques and various layer architectures
An autoencoder (AE) is a type of artificial neural network used to copy inputs to outputs by learning unlabeled data through unsupervised learning.

Decoding CNNs: A Deep Dive into Convolutional Neural Network Architectures
Explore how CNN architectures work, leveraging convolutional, pooling, and fully connected layers
While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the backbone of modern computer vision, their multi-layered complexity can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide deconstructs the CNN pipeline—from the mechanics of convolutional operations and spatial hierarchies to the evolution of landmark architectures like AlexNet and DenseNet.
Whether you're optimizing hyperparameters like stride and padding or choosing between 1D, 2D, and 3D variants, this post provides the technical clarity needed to master visual data processing.

Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Time Series Analysis
Managing temporal dependencies and sequential data using the RNN family, including LSTMs, GRUs, and state-space models.
Deep Dive into Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN): Mechanics, Math, and Limitations
Explore core of sequential data modeling and how standard RNNs handle temporal dependencies
From sequential data modeling with the chain rule to hands-on PyTorch simulations, learn why standard RNNs struggle with long-term dependencies and how the vanishing gradient problem manifests in real-time training.

Mastering Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks
Uncover how LSTM architecture outperforms standard RNNs in a real-world predictive modeling task
While standard RNNs struggle with long-term dependencies, LSTMs leverage a sophisticated gating mechanism to maintain information flow. This article breaks down LLM Fine-tuningematical core of forget, input, and output gates, explains the additive gradient path that prevents vanishing gradients, and provides a PyTorch implementation comparing LSTM and RNN performance on long-sequence weather data.

Understanding GRU Architecture and the Power of Path Signatures
An in-depth exploration of how GRUs solve the gradient problem and heavy computational overhead for modeling long sequences
A deep dive into LLM Fine-tuningematical mechanisms of GRUs, error signals, and how Signature GRUs (SigGRU) leverage temporal geometry for superior long-sequence forecasting.

A Deep Dive into Bidirectional RNNs, LSTMs, and GRUs
Explore how BRNNs handle contextual predictions over sequential data with practical examples
Standard RNNs often miss the context required for complex sequence modeling. This guide breaks down the mechanics of Bidirectional RNNs (BRNNs), provides a mathematical walkthrough, and uses PyTorch simulations to compare BiLSTM and BiGRU performance across varying sequence lengths.

Deep Recurrent Neural Networks: Engineering Depth for Complex Sequences
Explore how BRNNs handle contextual predictions over sequential data with practical examples
An in-depth technical exploration of DRNN architectures. Learn how to implement and optimize vertical, temporal, and I/O depth to handle high-dimensional sequential data in NLP and time-series forecasting.

Advanced Cross-Validation for Sequential Data: A Guide to Avoiding Data Leakage
Improve generalization capabilities while keeping data in order
Cross-validation (CV) is a statistical technique to evaluate generalization capabilities of a machine learning model.
Standard K-Fold fails on sequential data.
To avoid data leakage, we need to:
- Maintain temporal orders,
- Use time-series specific validation methods, and
- Prevent autocorrelation between training and validation datasets.
This technical deep dive explores specialized validation strategies—including Walk-Forward, Gap, and hv-Blocked CV—with a performance simulation comparing PyTorch GRU and Scikit-Learn SVR models.

Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Deep Learning (Discriminative)
Mastering multi-layer perceptrons (MLP) and feed-forward networks for complex feature extraction and classification.
Beyond the Black Box: Architecting Deep Feedforward Networks with NumPy
Deep Dive into Feedforward Architectures with Math and Code
While high-level frameworks make deep learning accessible, true mastery lies in understanding the underlying calculus and linear algebra. This guide breaks down Deep Feedforward Networks (DFNs) into their fundamental components—from He Initialization and ReLU activations to L2 regularization and Adam optimization—providing a step-by-step mathematical derivation and a robust Python implementation from scratch.

Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Traditional ML (Statistical Learning)
This section covers traditional supervised algorithms, each grounded in their mathematical foundations and practical coding implementations:
- Complexity (generalization bounds, hyperparameter tuning),
- Task robustness (ability to handle both regression and classification),
- Data robustness (ability to handle mixed, high-dimensional, or non-convex data), and
- Inherent assumptions (e.g., parametric or non-parametric).
Mastering the Bias-Variance Trade-Off: An Empirical Study of VC Dimension and Generalization Bounds
How model complexity and data size impact generalization performance in machine learning
While the bias-variance trade-off is a familiar hurdle in supervised learning, the Vapnik-Chervonenkis (VC) dimension offers the mathematical rigor needed to quantify a model's capacity.
This article evaluates the relationship between the VC dimension, VC bounds, and generalization error through empirical testing on synthetic datasets, demonstrating how theoretical limits translate to real-world model performance.

Regression Loss Functions & Regularization
Navigating model complexity and practical frameworks for model selection in regression problems
Regression is a common task in machine learning with variety of applications.
The learning problem of regression is to identify the most suitable approximate function (hypothesis) that can accurately map input values X to output values Y:

A Deep Dive into KNN Optimization and Distance Metrics
Strategies for distance computation and optimal "k" selection
K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) is often the first algorithm we learn, but mastering it requires navigating the bias-variance tradeoff and the curse of dimensionality. This technical guide explores the mechanics of unweighted vs. weighted KNN, compares six critical distance metrics (from Minkowski to Jaccard), and demonstrates how to leverage K-fold cross-validation and Grid Search to find LLM Fine-tuningematically optimal k for your dataset.

Mastering Decision Trees: From Impurity Measures to Greedy Optimization
Explore the core of decision tree mechanics with practical walkthrough examples, math, and coding implementation
An in-depth technical guide to decision tree algorithms. Learn LLM Fine-tuningematical foundations of $E(D)$ and $G(D)$, explore how greedy algorithms find optimal splits, and see a comparative simulation of Exact vs. Histogram-based methods using Scikit-Learn.

Gradient Boosting Decoded: From Mathematical Foundations to Competitive Benchmarks
Explore core concepts and practical implementations for enhanced performance.
An in-depth technical guide to Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM). This article bridges the gap between theoretical loss minimization—using negative gradients and pseudo-residuals—and practical application. We implement a custom GBM from scratch and benchmark industry leaders like XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost against traditional Logistic Regression and Deep Learning models.

Random Forest Decoded: Architecture, Bagging, and Performance Benchmarks
Explore architecture, optimization strategies, and practical implications.
An in-depth technical exploration of Random Forest ensembles. This article covers the mechanics of bootstrapping and feature selection, explains Out-of-Bag (OOB) error estimation, and provides a head-to-head Python simulation comparing Random Forest complexity against Gradient Boosting Machines (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost) for classification tasks.

Building Powerful Naive Bayes Ensembles for Mixed Datasets
Explore an ensemble approach to make Naive Bayes more robust to complex datasets
Naive Bayes is often sidelined due to its native feature independence assumption. However, by leveraging specialized pipelines for Gaussian, Bernoulli, and Multinomial data—and combining them via stacking—you can build a high-efficiency classifier that handles complex, real-world datasets with minimal overhead.

Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass