Advanced LLM Engineering & Neural Architecture
Advanced technical guides on LLM fine-tuning, transformer mechanisms (LoRA, GQA, RoPE), and NLP, the engineering of linguistic models.
A comprehensive technical index exploring the frontier of Large Language Models. From foundational Transformer mechanisms and tokenization strategies to advanced fine-tuning (SFT, DPO) and inference optimization, these guides provide the mathematical and architectural rigor required for production-scale ML systems.
Categories
- LLM Engineering:
Alignment and fine-tuning techniques like SFT, DPO, KL Divergence, and LoRA. - Benchmarking & Inference:
Exploring reasoning walls, decoding strategies, context windows, and RAG. - Transformer Architectural Deep Dives:
Explore foundational transformer architectures such as self-attention, GQA, PE, and tokenization. - Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Engineering systems for linguistic understanding, from word embeddings and NER to advanced semantic analysis.
LLM Engineering
Engineering systems for linguistic understanding, from word embeddings and NER to advanced semantic analysis.
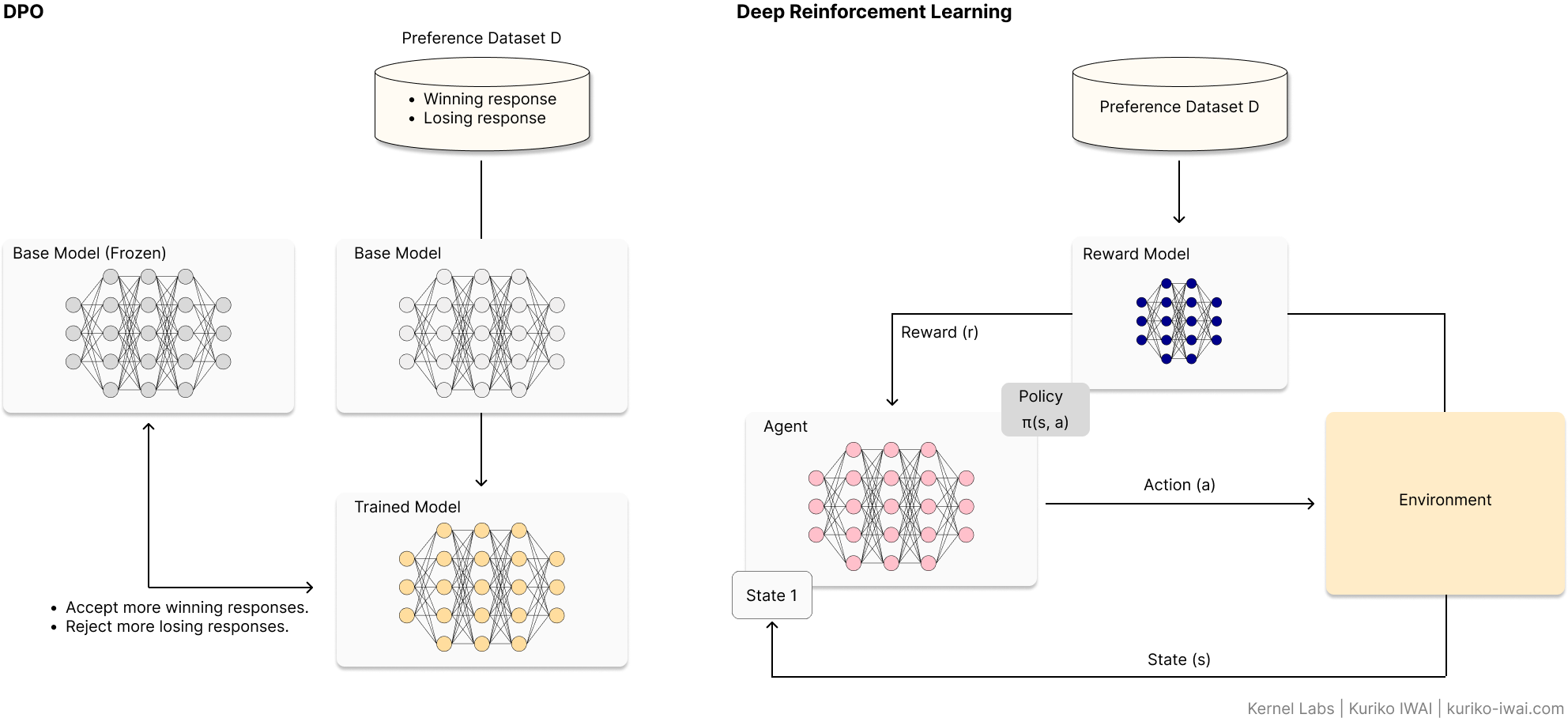
Aligning LLMs with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)
Learn the fundamentals and follow a technical walkthrough with Unsloth and Llama.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has long been the gold standard for LLM alignment, but its complexity—requiring separate reward models and unstable PPO loops—is a significant barrier.
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) simplifies this by treating alignment as a direct classification problem.
This article breaks down the mathematical foundation of DPO, provides a hands-on implementation guide using the Unsloth framework, and explores the strategic trade-offs between DPO and traditional RLHF.
Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
A Technical Guide to QLoRA and Memory-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Master how QLoRA enables 70B model tuning on consumer GPUs, leveraging NF4, Double Quantization, and Paged Optimizers.
As Large Language Models scale, the hardware requirements for fine-tuning have become prohibitive for the average developer.
Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation (QLoRA) changes the game by shrinking VRAM requirements by over 95%.
This deep dive explores the core mechanics—NormalFloat 4 (NF4), Double Quantization, and Paged Optimizers—that allow a 70B parameter model to be tuned on a single 48GB GPU without sacrificing 16-bit performance levels.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Is 4-Bit All You Need? The Math Behind Modern LLM Compression
The Engineer’s Guide to LLM Quantization. Learn How Quantization Makes 70B Models Run on Local GPU.
An technical exploration of numerical precision in Large Language Models.
This article deconstructs standard FP32 formats and evaluates modern quantization schemes—including Integer, NormalFloat, and Microscaling—to help developers balance computational efficiency with model fidelity.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Scaling Securely - A Technical Deep Dive into AWS VPC Architecture for MLOps
Master AWS VPC for Machine Learning and MLOps with Practical Use Cases.
As Large Language Models (LLMs) transition from research to production, the security frontier has shifted to the network layer.
This technical guide explores how to architect an AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) specifically for ML workloads.
I move beyond theory to provide step-by-step CLI configurations for four critical use cases: from cost-efficient tabular pipelines to high-performance distributed LLM training using Elastic Fabric Adapters (EFA).
Learn how to eliminate data egress fees and harden your infrastructure against unauthorized access.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Building LoRA Multi-Adapter Inference on AWS SageMaker
Decoupling Weights for Scale: A Guide to Dynamic Multi-Adapter Orchestration.
This technical guide explores the implementation of high-density LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) multi-adapter inference.
I demonstrate how to move away from costly dedicated model endpoints toward a unified architecture using Amazon SageMaker Multi-Model Endpoints (MME).
By decoupling the heavy base model weights from lightweight task-specific adapters, developers can achieve a 96% reduction in overhead while maintaining low-latency switching across divergent domains like medical documentation, sales schema enforcement, and linguistic localization.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Deconstructing LoRA: The Math and Mechanics of Low-Rank Adaptation
Master the math of rank decomposition, hyperparameter tuning, and tips to avoid common pitfalls
While big tech uses massive clusters for LLM tuning, the real world requires VRAM efficiency.
This deep dive explores Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), explaining how it achieves full-tuned performance with 1/10,000th of the expense.
Using Qwen-3-1.7B as a reference, we break down the linear algebra of rank decomposition, provide a guide for tuning hyperparameters (r and alpha), and address critical security pitfalls like data-centric and extraction attacks.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
The Definitive Guide to LLM Fine-Tuning: Objectivee, Mechanisms, and Hardware
Master LLM fine-tuning with the framework for base model selection, tuning mechanisms, and hardware constraints
A comprehensive technical deep-dive into the methodologies of fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs).
This guide breaks down the transition from foundation models to task-specific experts, covering learning objectives like SFT and DPO, and efficient architectural mechanisms including LoRA, QLoRA, and ReFT.
Ideal for developers looking to optimize model performance while balancing GPU constraints and data requirements.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Regularizing LLMs with Kullback-Leibler Divergence
Master the exploration-exploitation trade-off in fine-tuning with KL divergence regularization
A deep dive into the mechanics of KL Divergence in machine learning. This article examines the geometric properties of the Bregman family, the asymmetric traits of forward vs. reverse KL, and practical PyTorch implementations for preventing policy collapse during fine-tuning.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Benchmarking & Inference
The Reasoning Wall: A Comparative Benchmark of Llama 3.2 vs. Qwen 3
Stress-testing multi-hop logic chains using Multi-LogiEval, Process Benchmarking, and Thought-to-Output Ratios
Most LLM benchmarks fail to identify exactly where logical coherence collapses.
This report establishes a framework for measuring Reasoning Depth (d) across three task tiers. By evaluating Llama 3.2 and Qwen 3 through four granular metrics—including Robustness Coefficients and Thought-to-Output ratios—we identify the reasoning wall and provide architectural recommendations for production-scale deployment.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
LLM Decoding Strategies: A Guide to Algorithms and Sampling Methods
Discover how major decoding methods and algorithms work and their usages with practical examples
A Large Language Model (LLM), especially those with a decoder-only architecture, is a system designed to generate text that mirrors human-like fluency and coherence.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
DoLa Decoding: Mitigating LLM Hallucinations via Layer Contrast
Explore how DoLA (Decoding by Contrasting Layers) mitigates hallucinations in transformer-based LMs
Decoding by Contrasting Layers (DoLa) is an inference-time decoding method that enhances a model’s factual knowledge by intervening in the conditional probability step.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Optimizing LLM Performance: Context Window Impact on RAG Accuracy
Benchmarking context length for optimal accuracy in long-form retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)
The context window (or context length) defines the maximum number of tokens — including the input prompt, any system instructions, and the model’s generated response — that the LLM can simultaneously process and attend to during the autoregressive loop.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Transformer Architectural Deep Dives
Tokenization Strategies for LLM Applications
Explore the mechanics like BPE and Unigram and how to choose suitable tokenizer for your LLM application
Tokenization is the bridge between human language and machine-readable vectors.
Choosing the right tokenizer impacts an LLM's capabilities. This technical guide breaks down the core architectures and provides a framework for selecting the best one for your task.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Transformer Architecture: Self-Attention & MLOps Guide
Exploring attention and its role in contextual text understanding with walkthrough examples
The transformer model revolutionizes natural language processing (NLP) by processing entire sequences at once, leveraging techniques like self-attention mechanism, positional encodings, and multi-head attention.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Beyond the Window: Benchmarking Positional Encoding (PE) for LLM Extrapolation
Scaling context windows via PE extrapolation on unseen sequence lengths
An architectural deep dive and synthetic benchmark of FAPE, LPE, RPE, and RoPE. Learn how different Positional Encoding methods impact a Transformer's ability to handle sequences 20x longer than its training context.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Grouped Query Attention (GQA): Balancing LLM Quality and Speed
Finding the perfect balance between MHA quality and MQA inference throughput
Grouped-Query Attention (GQA) is a type of attention mechanisms designed to reduce the memory bandwidth requirements and latency during the decoding phase.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Implementing Attention Approximation: Transformer Efficiency & Trade-offsr
Self-attention mechanisms and attention approximation techniques in Transformer
The Transformer architecture, introduced in the “Attention Is All You Need” paper, has revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP). Its core innovation, the self-attention mechanism, allows models to weigh the importance of different parts of the input sequence. However, the standard self-attention mechanism suffers from its computational complexity which scales quadratically (O(N²)) as the length of the input sequence N grows, creating a bottleneck especially in tasks with long N such as document summarization or high-resolution image processing. Attention approximation solve this challenge by reducing the complexity using various techniques.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Engineering systems for linguistic understanding, from word embeddings and NER to advanced semantic analysis.
LLM Decoding Strategies: A Guide to Algorithms and Sampling Methods
Discover how major decoding methods and algorithms work and their usages with practical examples
A Large Language Model (LLM), especially those with a decoder-only architecture, is a system designed to generate text that mirrors human-like fluency and coherence.

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Beyond Zero: A Guide to N-Gram Smoothing and Language Model Robustness
Practical applications of key smoothing algorithms in n-gram models
Discover why zero-frequency events break NLP models and how to implement smoothing strategies—from simple Add-k to state-of-the-art Kneser-Ney—to ensure your language models handle unseen data gracefully

Kernel Labs | Kuriko IWAI | kuriko-iwai.com
Looking for Solutions?
- Deploying ML Systems 👉 Book a briefing session
- Hiring an ML Engineer 👉 Drop an email
- Learn by Doing 👉 Enroll AI Engineering Masterclass